Email: [email protected]
Cone Crusher vs. Gyratory Crusher
In mining, quarrying, and aggregate production, choosing the right crusher for primary and secondary stages is key to keeping costs down and running operations smoothly. Comparing cone crusher vs gyratory crusher is important for plant managers and engineers. While both use a cone-shaped crushing method, their designs, uses, and working features are quite different.

Side-by-Side Technical Comparison
Let’s see the differences at a glance:

How does a cone crusher differ from a Gyratory in plain terms?
Both cone crusher and Gyratory crusher work by crushing rocks between a moving part and a fixed part, but there are some key differences:
- Size & Usage:
Gyratory crusher is bigger and is mostly used as the first step to crush large, hard rocks in mining. A cone crusher is smaller, often used in later stages to turn smaller rocks into finer material. - Shape & Crushing Motion:
Gyratory crusher has a cone-shaped head that moves in a circular motion inside a deep, rounded bowl. This lets it handle very large pieces and push them down as they get crushed. A cone crusher squeezes rocks between a spinning mantle and a stationary bowl liner, with a movement that’s more elliptical, and it usually has a steeper chamber. - What They’re Best At:
Gyratory crusher is ideal for handling very large, tough rocks at high volumes, usually in the first crushing step. Cone crusher is better for producing smaller, more precise sizes after the big rocks have been broken down, typically in the second or third crushing steps. - Maintenance & Cost:
Gyratory crusher is larger, more complex, and cost more to maintain. Cone crusher tends to be simpler, cheaper to run, and easier to maintain.
Use a gyratory crusher for really big rocks and high capacity at the start of the process; use a cone crusher for smaller rocks and finer output further down the line.
When is a gyratory crusher preferred over a cone crusher?
A gyratory crusher is preferred over a cone crusher when you need to crush very large, tough rocks and require extremely high throughput, especially in primary (first-step) crushing in large mining operations.
Main Reasons to Choose a Gyratory Crusher
- Big Feed Size: Gyratory crusher handles much larger rock sizes, making them ideal when the incoming material is large boulders that need breaking down.
- High Capacity: They can process more material per hour than cone crusher, which is necessary for big, busy mines needing fast production.
- Robustness: Gyratory crusher is built stronger and are better for really hard, abrasive materials that would quickly wear out smaller machines.
- Continuous Primary Crushing: They’re excellent for the first crushing stage and create a uniform product size for further processing.

How throughput capacity compares between gyratory and cone?
Gyratory crusher can handle bigger rocks and have higher throughput capacity than cone crusher, making them ideal for heavy-duty, high-volume jobs like primary crushing in large mining operations. Cone crusher process smaller material and generally have lower capacity but can produce finer output and are more efficient for secondary or tertiary crushing.
Comparative Table: Throughput Capacity
- Gyratory crusher: Best when the operation demands breaking huge rocks and moving a massive amount of material quickly.
- Cone crusher: Better for detailed, final shaping and sizing at lower tonnages.
Gyratory crusher is the go-to choice for top-end capacity, while cone crusher excel in finer, more controlled output with less throughput.
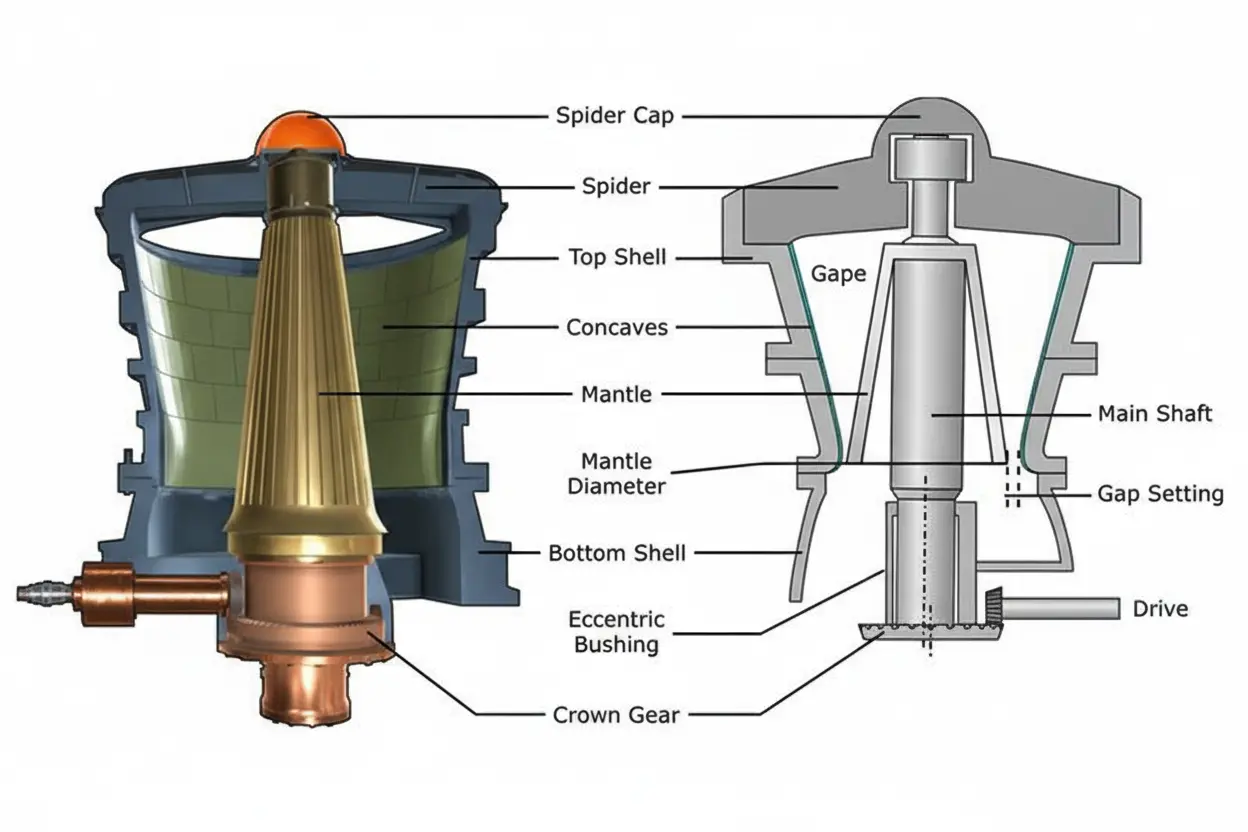
In-depth Design & Operation Differences
Crushing Mechanism
- Gyratory Crusher: The entire head moves in a circular motion, providing continuous crushing as large rocks are pressed and broken.
- Cone Crusher: Utilizes a squeezing action via an oscillating cone, most effective with smaller feed and producing a finer product.
Speed & Force
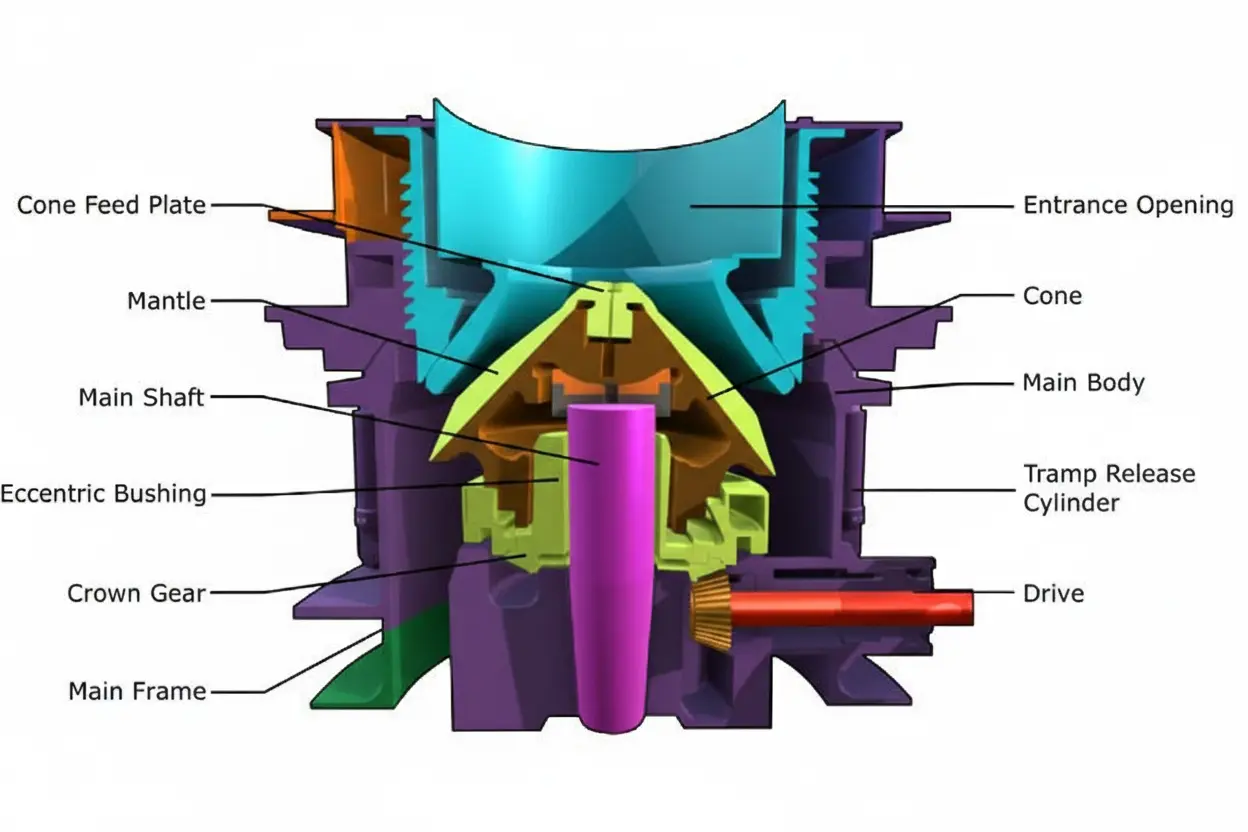
Performance, Efficiency, and Cost Factors
Throughput & Efficiency
Gyratory crusher can process substantially larger volumes and massive rock, but often at higher energy and maintenance cost. Cone crusher, with their steeper chambers and faster cycling, is generally more energy-efficient for smaller aggregate production.
Product Quality
Maintenance & Reliability
- Gyratory: More downtime for routine maintenance (liner changes, shaft adjustments). Service is almost always via the top; space and lift equipment are needed.
- Cone: Easier forced lubrication, modern hydraulic automated settings, more accessible wear part replacement, and overall cheaper to maintain.
Typical Product Specifications for Reference
| Model | Max Feed Size | Output Size | Capacity (TPH) | Motor Power (kW) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HST Cone Crusher | 275mm | 4-41mm | 45-2130 | 90-630 |
| HPT Multi-cylinder | 330mm | 6-38mm | 100-790 | 110-500 |
| CS Spring Cone | 278mm | 3-64mm | 27-1400 | 75-400 |
| Gyratory Crusher | 1200mm* | 150mm* | Up to 5000* | 300–1000* |
*Representative industry values; actual specs depend on manufacturer and model.
Selecting between a cone crusher vs. gyratory crusher means balancing feed, throughput, space, cost, and product requirements. Make a choice aligned with long-term goals for reliability, efficiency, and high-quality output. Don’t hesitate to reach out to engineers or trusted suppliers for tailored recommendations—they can help you avoid expensive mistakes and boost your bottom line.




